The Atkins diet is a low-carbohydrate diet, usually recommended for weight loss.
Proponents of this diet claim that you can lose weight eating as much protein and fat as you want, as long as you avoid foods high in carbs.
In the past 12 years, over 20 studies have shown that low-carb diets are effective for weight loss (without calorie counting), and can lead to various health improvements.
The Atkins diet was originally promoted by a physician named Dr. Robert C. Atkins, who wrote a best-selling book about the diet in 1972.
Since then, the Atkins diet has been popular all over the world and many more books have been written about it.
The diet was originally considered unhealthy and demonized by the mainstream health authorities, mostly due to the high saturated fat content. However, new studies have shown that saturated fat is harmless (1, 2).
Since then, the diet has been studied thoroughly and shown to lead to more weight loss than low-fat diets, and greater improvements in blood sugar, HDL (the "good" cholesterol), triglycerides and other health markers (3, 4).
Despite being high in fat, it does not raise LDL (the "bad") cholesterol on average, although this does happen in a subset of individuals (5).
The main reason low-carb diets are so effective for weight loss, is that when people reduce carbohydrate intake and eat more protein, their appetite goes down and they end up automatically eating fewer calories without having to think about it (6, 7).
You can read more about the health benefits of low-carb diets in this article.
The Atkins Diet Is a 4-Phase Plan
The Atkins diet is split into 4 different phases:
- Phase 1 (induction): Under 20 grams of carbs per day for 2 weeks. Eat high-fat, high-protein, with low-carb vegetables like leafy greens. This kick-starts the weight loss.
- Phase 2 (balancing): Slowly add more nuts, low-carb vegetables and small amounts of fruit back to your diet.
- Phase 3 (fine-tuning): When you are very close to your goal weight, add more carbs to your diet until weight loss slows down.
- Phase 4 (maintenance): Here you can eat as many healthy carbs as your body can tolerate without regaining weight.
However, these phases are a bit complicated and may not be necessary. You should be able to lose weight and keep it off as long as you stick to the meal plan below.
Some people choose to skip the induction phase altogether and include plenty of vegetables and fruit from the start. This approach can be very effective as well.
Others prefer to just stay in the induction phase indefinitely. This is also known as a very low-carb ketogenic diet (keto).
Foods to Avoid
You should avoid these foods on the Atkins diet:
- Sugar: Soft drinks, fruit juices, cakes, candy, ice cream, etc.
- Grains: Wheat, spelt, rye, barley, rice.
- Vegetable oils: Soybean oil, corn oil, cottonseed oil, canola oil and a few others.
- Trans fats: Usually found in processed foods with the word "hydrogenated" on the ingredients list.
- "Diet" and "low-fat" foods: These are usually very high in sugar.
- High-carb vegetables: Carrots, turnips, etc (induction only).
- High-carb fruits: Bananas, apples, oranges, pears, grapes (induction only).
- Starches: Potatoes, sweet potatoes (induction only).
- Legumes: Lentils, beans, chickpeas, etc (induction only).
Foods to Eat
You should base your diet around these healthy foods.
- Meats: Beef, pork, lamb, chicken, bacon and others.
- Fatty fish and seafood: Salmon, trout, sardines, etc.
- Eggs: The healthiest eggs are Omega-3 enriched or pastured.
- Low-carb vegetables: Kale, spinach, broccoli, asparagus and others.
- Full-fat dairy: Butter, cheese, cream, full-fat yoghurt.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, macadamia nuts, walnuts, sunflower seeds, etc.
- Healthy fats: Extra virgin olive oil, coconut oil, avocados and avocado oil.
As long as you base your meals around a fatty protein source with vegetables or nuts and some healthy fats, then you will lose weight. It's that simple.
After Induction Is Over, You Can Slowly Add Back Healthier Carbs
Despite what you may have heard, the Atkins diet is actually quite flexible.
It is only during the 2-week induction phase that you need to minimize your intake of healthier carb sources.
After induction is over, you can slowly add back healthier carbs such as higher carb vegetables, fruits, berries, potatoes, legumes and healthier grains like oats and rice.
However, chances are that you will need to stay moderately low-carb for life, even if you reach your weight loss goals.
If you start eating the same old foods again in the same amounts as before, you will gain back the weight. This is true of any weight loss diet.
Maybe Eat
There are many delicious foods you can eat on the Atkins diet.
This includes foods like bacon, heavy cream, cheese and dark chocolate.
Many of these are generally considered fattening because of the high fat and calorie content.
However, when you're on a low-carb diet, fat becomes your body's preferred energy source, making these foods perfectly acceptable.
Drink
Here are some drinks that are acceptable on the Atkins diet.
- Water: As always, water should be your go-to beverage.
- Coffee: Despite what you may have heard, coffee is high in antioxidants and actually quite healthy.
- Green tea: A very healthy beverage.
Alcohol is also fine in small amounts. Stick to dry wines with no added sugars, and avoid high-carb drinks like beer.
What About Vegetarians?
It is possible to do the Atkins diet as a vegetarian (and even vegan), but difficult.
You can use soy-based foods for protein and eat plenty of nuts and seeds. Olive oil and coconut oil are excellent plant-based fat sources.
Lacto-ovo-vegetarians can also eat eggs, cheese, butter, heavy cream and other high-fat dairyfoods.
A Sample Atkins Menu For One Week
This is a sample menu for one week on the Atkins diet.
It is suitable for the induction phase, but you should add more higher-carb vegetables and some fruits as you move on to the other phases.
Monday
- Breakfast: Eggs and vegetables, fried in coconut oil.
- Lunch: Chicken salad with olive oil, and a handful of nuts.
- Dinner: Steak and veggies.
Tuesday
- Breakfast: Bacon and eggs.
- Lunch: Leftover chicken and veggies from the night before.
- Dinner: Cheeseburger (without the bun), with vegetables and butter.
Wednesday
- Breakfast: Omelet with veggies, fried in butter.
- Lunch: Shrimp salad with some olive oil.
- Dinner: Ground beef stir fry, with veggies.
Thursday
- Breakfast: Eggs and veggies, fried in coconut oil.
- Lunch: Leftover stir fry from dinner the night before.
- Dinner: Salmon with butter and vegetables.
Friday
- Breakfast: Bacon and eggs.
- Lunch: Chicken salad with olive oil and a handful of nuts.
- Dinner: Meatballs with vegetables.
Saturday
- Breakfast: Omelet with various vegetables, fried in butter.
- Lunch: Leftover meatballs from the night before.
- Dinner: Pork chops with vegetables.
Sunday
- Breakfast: Bacon and eggs.
- Lunch: Leftover pork chops from the night before.
- Dinner: Grilled chicken wings, with some salsa and veggies.
Make sure to include a variety of different vegetables in your diet.
Healthy Low-Carb Snacks
Most people feel that their appetite goes down on the Atkins diet.
They tend to feel more than satisfied with 3 meals per day (sometimes only 2).
However, if you feel hungry between meals, then here are a few quick healthy snacks:
- Leftovers.
- A hard-boiled egg or two.
- A piece of cheese.
- A piece of meat.
- A handful of nuts.
- Some greek yogurt.
- Berries and whipped cream.
- Baby carrots (careful during induction).
- Fruits (after induction).
How to Follow The Atkins Diet When Eating Out
It is actually very easy to follow the Atkins diet at most restaurants.
- Get extra vegetables instead of bread, potatoes or rice.
- Order a meal based on fatty meat or fatty fish.
- Get some extra sauce, butter or olive oil with your meal.
A Simple Shopping List For The Atkins Diet
It is a good rule to shop at the perimeter of the store. This is usually where the whole foods are found.
Eating organic is not necessary, but always go for the least processed option that fits into your price range.
- Meats: Beef, chicken, lamb, pork, bacon.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, trout, etc.
- Shrimp and shellfish.
- Eggs.
- Dairy: Greek yogurt, heavy cream, butter, cheese.
- Vegetables: Spinach, kale, lettuce, tomatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, onions, etc.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, etc.
- Nuts: Almonds, macadamia nuts, walnuts, hazelnuts, etc.
- Seeds: Sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, etc.
- Fruits: Apples, pears, oranges.
- Coconut oil.
- Olives.
- Extra virgin olive oil.
- Dark chocolate.
- Avocados.
- Condiments: Sea salt, pepper, turmeric, cinnamon, garlic, parsley, etc.
It is highly recommended to clear your pantry of all unhealthy foods and ingredients. This includes ice cream, sodas, breakfast cereals, breads, juices and baking ingredients like sugar and wheat flour.
You Won't Be Disappointed
If you're serious about the Atkins diet, I recommend you get one of the Atkins books and simply get started as soon as possible.
That being said, the detailed guide in this article should contain everything you need to succeed.
At the end of the day, the Atkins diet is a very healthy and effective way to lose weight. You won't be disappointed.
Are Atkins Low-Carb Bars Healthy? A Critical Look
I've gotten several e-mails asking me about the low-carb bars made by the Atkins company.
These include Atkins Advantage Bars and Atkins Endulge Bars.
These products are marketed as low-carb friendly meal replacements.
Before I get into this post, I'd like to point out that the late Dr. Atkins really had nothing to do with this stuff.
He died in the year 2003 and the company that markets these products is now owned by some giant corporation.
I'm a big believer in low-carb diets. I honestly believe that they are a potential cure for some of the world's biggest health problems.
In fact, the research agrees with me. Over 20 randomized controlled trials prove that low-carb diets are an excellent option to treat obesity and metabolic problems like diabetes (1, 2, 3).
They are certainly a much better option than the low-fat diet that is still recommended by the mainstream nutrition organizations, which is notoriously ineffective (4, 5).
However, I don't think that the "low-carb" aspect is the only reason these diets work so well.
One of the key reasons these diets are so effective, is that they encourage people to eat real, unprocessed foods instead of the processed foods they were eating before.
Unfortunately, the Atkins bars are not "real" foods. They are highly processed products made in factories.
Even though these bars are technically "low-carb" - I don't think you should be consuming them. Let me explain why...
You can learn a lot about a food product by looking at the ingredients list.
The best foods are those that don't even need an ingredients list. That means that they are unprocessed, whole foods.
Take a look at the ingredients list for an Atkins Advantage bar:
Does that look like food to you?
It is obvious that there is very little actual food in there. This product is made solely from highly refined ingredients and artificial chemicals.
A few important things can be learned from this ingredients list:
- Artificial flavor. This is listed twice and implies that there are many additional artificial chemicals in there.
- Soy. There are several soy-derived products in there, which may cause a number of problems.
- Vitamins and minerals. Be aware that the "nutrients" in there are NOT present naturally in the bars. They are synthetic, factory-made nutrients that are added to them.
- Sugar alcohols. Atkins bars are sweetened with maltitol, a sugar alcohol that has minor effects on blood sugar and can cause digestive issues (6).
- Artificial sweeteners. Although controversial, there is some evidence that artificial sweetener use can contribute to weight gain and other problems (7).
Really... these bars aren't food. They are highly processed products with a massive range of artificial chemicals, some of which are potentially harmful.
Processed low-carb products often have labels saying that they contain a certain amount of "net carbs."
These products usually contain a significant amount of carbohydrate, but a large part of these carbs are indigestible.
This includes fiber and certain sugar alcohols.
However... it's important to keep in mind that food manufacturers often deceive people with their labeling.
The "net carb" claim is NOT regulated by the FDA or any regulatory agency and cannot be trusted.
There are many cases of so-called "low carb" products being able to raise blood sugar just as much as their regular counterparts.
No actual study has ever been done on the health effects of the Atkins bars, but I did look at several chat forums and many people report having digestive issues and stalled weight loss after consuming them.
These bars might be fine as an occasional treat, or something to keep in your glove compartment in case you're out on the road and can't find a healthy low-carb meal anywhere.
You could probably eat them every now and then without "breaking" your low-carb diet and knocking yourself out of ketosis.
However, it would be much better to spend your calorie budget on real, unprocessed foods... foods that aren't made in factories and actually contain natural ingredients, like meat and veggies.
At the end of the day, low-carb junk food is still junk food. Period.
23 Studies on Low-Carb and Low-Fat Diets — Time to Retire The Fad
Few things have been debated as much as "carbohydrates vs fat."
Some believe that increased fat in the diet is a leading cause of all kinds of health problems, especially heart disease.
This is the position maintained by most mainstream health organizations.
These organizations generally recommend that people restrict dietary fat to less than 30% of total calories (a low-fat diet).
However... in the past 11 years, an increasing number of studies have been challenging the low-fat dietary approach.
Many health professionals now believe that a low-carb diet (higher in fat and protein) is a much better option to treat obesity and other chronic, Western diseases.
In this article, I have analyzed the data from 23 of these studies comparing low-carb and low-fat diets.
All of the studies are randomized controlled trials, the gold standard of science. All are published in respected, peer-reviewed journals.
Most of the studies are being conducted on people with health problems, including overweight/obesity, type II diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Keep in mind that these are the biggest health problems in the world.
The main outcomes measured are usually weight loss, as well as common risk factors like Total Cholesterol, LDL Cholesterol, HDL Cholesterol, Triglycerides and Blood Sugar levels.
1. Foster GD, et al. A randomized trial of a low-carbohydrate diet for obesity. New England Journal of Medicine, 2003.
Details: 63 individuals were randomized to either a low-fat diet group, or a low-carb diet group. The low-fat group was calorie restricted. This study went on for 12 months.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost more weight, 7.3% of total body weight, compared to the low-fat group, which lost 4.5%. The difference was statistically significant at 3 and 6 months, but not 12 months.
Conclusion: There was more weight loss in the low-carb group, significant at 3 and 6 months, but not 12. The low-carb group had greater improvements in blood triglycerides and HDL, but other biomarkers were similar between groups.
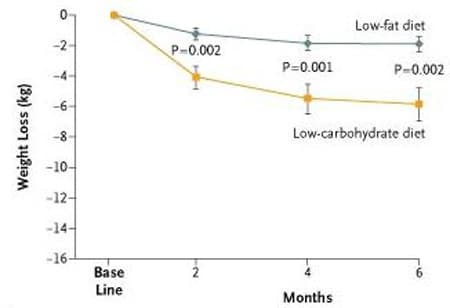
2. Samaha FF, et al. A low-carbohydrate as compared with a low-fat diet in severe obesity.New England Journal of Medicine, 2003.
Details: 132 individuals with severe obesity (mean BMI of 43) were randomized to either a low-fat or a low-carb diet. Many of the subjects had metabolic syndrome or type II diabetes. The low-fat dieters were calorie restricted. Study duration was 6 months.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost an average of 5.8 kg (12.8 lbs) while the low-fat group lost only 1.9 kg (4.2 lbs). The difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost significantly more weight (about 3 times as much). There was also a statistically significant difference in several biomarkers:
- Triglycerides went down by 38 mg/dL in the LC group, compared to 7 mg/dL in the LF group.
- Insulin sensitivity improved on LC, got slightly worse on LF.
- Fasting blood glucose levels went down by 26 mg/dL in the LC group, only 5 mg/dL in the LF group.
- Insulin levels went down by 27% in the LC group, but increased slightly in the LF group.
Overall, the low-carb diet had significantly more beneficial effects on weight and key biomarkers in this group of severely obese individuals.
3. Sondike SB, et al. Effects of a low-carbohydrate diet on weight loss and cardiovascular risk factor in overweight adolescents. The Journal of Pediatrics, 2003.
Details: 30 overweight adolescents were randomized to two groups, a low-carb diet group and a low-fat diet group. This study went on for 12 weeks. Neither group was instructed to restrict calories.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 9.9 kg (21.8 lbs), while the low-fat group lost 4.1 kg (9 lbs). The difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost significantly more (2.3 times as much) weight and had significant decreases in Triglycerides and Non-HDL cholesterol. Total and LDL cholesterol decreased in the low-fat group only.
4. Brehm BJ, et al. A randomized trial comparing a very low carbohydrate diet and a calorie-restricted low fat diet on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors in healthy women. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2003.
Details: 53 healthy but obese females were randomized to either a low-fat diet, or a low-carb diet. Low-fat group was calorie restricted. The study went on for 6 months.
Weight Loss: The women in the low-carb group lost an average og 8.5 kg (18.7 lbs), while the low-fat group lost an average of 3.9 kg (8.6 lbs). The difference was statistically significant at 6 months.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost more weight (2.2 times as much) and had significant reductions in blood triglycerides. HDL improved slightly in both groups.
5. Aude YW, et al. The national cholesterol education program diet vs a diet lower in carbohydrates and higher in protein and monounsaturated fat. Archives of Internal Medicine, 2004.
Details: 60 overweight individuals were randomized to a low-carb diet high in monounsaturated fat, or a low-fat diet based on the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP).
Both groups were calorie restricted and the study went on for 12 weeks.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost an average of 6.2 kg (13.6 lbs), while the low-fat group lost 3.4 kg (7.5 lbs). The difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost 1.8 times as much weight. There were also several changes in biomarkers that are worth noting:
- Waist-to-hip ratio is a marker for abdominal fat. This marker improved slightly in the LC group, not in the LF group.
- Total cholesterol improved in both groups.
- Triglycerides went down by 42 mg/dL in the LC group, compared to 15.3 mg/dL in the LF group.
- LDL particle size increased by 4.8 nm and percentage of small, dense LDL decreased by 6.1% in the LC group, while there was no significant difference in the LF group.
Overall, the low-carb group lost more weight and had much greater improvements in several important risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
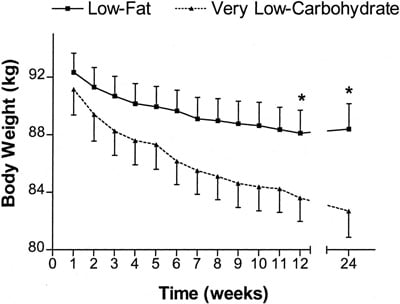
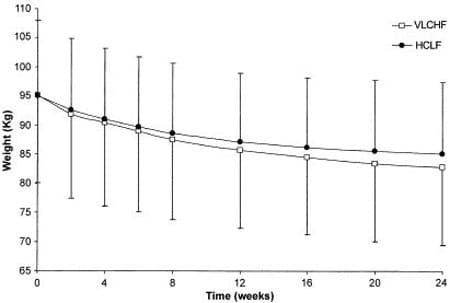
6. Yancy WS Jr, et al. A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-fat diet to treat obesity and hyperlipidemia. Annals of Internal Medicine, 2004.
Details: 120 overweight individuals with elevated blood lipids were randomized to a low-carb or a low-fat diet. The low-fat group was calorie restricted. Study went on for 24 weeks.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 9.4 kg (20.7 lbs) of their total body weight, compared to 4.8 kg (10.6 lbs) in the low-fat group.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost significantly more weight and had greater improvements in blood triglycerides and HDL cholesterol.
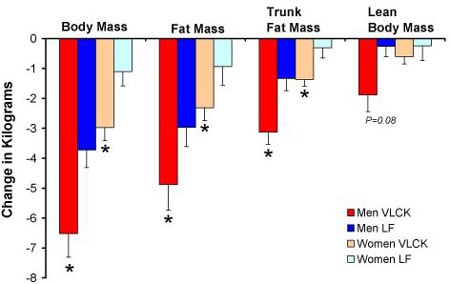
7. JS Volek, et al. Comparison of energy-restricted very low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets on weight loss and body composition in overweight men and women. Nutrition & Metabolism (London), 2004.
Details: A randomized, crossover trial with 28 overweight/obese individuals. Study went on for 30 days (for women) and 50 days (for men) on each diet, that is a very low-carb diet and a low-fat diet. Both diets were calorie restricted.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost significantly more weight, especially the men. This was despite the fact that they ended up eating more calories than the low-fat group.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost more weight. The men on the low-carb diet lost three times as much abdominal fat as the men on the low-fat diet.
8. Meckling KA, et al. Comparison of a low-fat diet to a low-carbohydrate diet on weight loss, body composition, and risk factors for diabetes and cardiovascular disease in free-living, overweight men and women. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2004.
Details: 40 overweight individuals were randomized to a low-carb and a low-fat diet for 10 weeks. The calories were matched between groups.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 7.0 kg (15.4 lbs) and the low-fat group lost 6.8 kg (14.9 lbs). The difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: Both groups lost a similar amount of weight.
A few other notable differences in biomarkers:
- Blood pressure decreased in both groups, both systolic and diastolic.
- Total and LDL cholesterol decreased in the LF group only.
- Triglycerides decreased in both groups.
- HDL cholesterol went up in the LC group, but decreased in the LF group.
- Blood sugar went down in both groups, but only the LC group had decreases in insulinlevels, indicating improved insulin sensitivity.
9. Nickols-Richardson SM, et al. Perceived hunger is lower and weight loss is greater in overweight premenopausal women consuming a low-carbohydrate/high-protein vs high-carbohydrate/low-fat diet. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 2005.
Details: 28 overweight premenopausal women consumed either a low-carb or a low-fat diet for 6 weeks. The low-fat group was calorie restricted.
Weight Loss: The women in the low-carb group lost 6.4 kg (14.1 lbs) compared to the low-fat group, which lost 4.2 kg (9.3 lbs). The results were statistically significant.
Conclusion: The low-carb diet caused significantly more weight loss and reduced hunger compared to the low-fat diet.
10. Daly ME, et al. Short-term effects of severe dietary carbohydrate-restriction advice in Type 2 diabetes. Diabetic Medicine, 2006.
Details: 102 patients with Type 2 diabetes were randomized to a low-carb or a low-fat diet for 3 months. The low-fat group was instructed to reduce portion sizes.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 3.55 kg (7.8 lbs), while the low-fat group lost only 0.92 kg (2 lbs). The difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost more weight and had greater improvements in the Total cholesterol/HDL ratio. There was no difference in triglycerides, blood pressure or HbA1c (a marker for blood sugar levels) between groups.
11. McClernon FJ, et al. The effects of a low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet and a low-fat diet on mood, hunger, and other self-reported symptoms. Obesity (Silver Spring), 2007.
Details: 119 overweight individuals were randomized to a low-carb, ketogenic diet or a calorie restricted low-fat diet for 6 months.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 12.9 kg (28.4 lbs), while the low-fat group lost only 6.7 kg (14.7 lbs).
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost almost twice the weight and experienced less hunger.
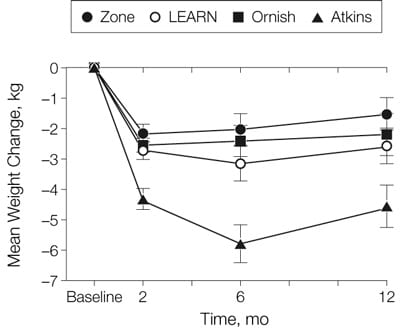
12. Gardner CD, et al. Comparison of the Atkins, Zone, Ornish, and LEARN diets for change in weight and related risk factors among overweight premenopausal women: the A TO Z Weight Loss Study. The Journal of The American Medical Association, 2007.
Details: 311 overweight/obese premenopausal women were randomized to 4 diets: A low-carb Atkins diet, a low-fat vegetarian Ornish diet, the Zone diet and the LEARN diet. Zone and LEARN were calorie restricted.
Weight Loss: The Atkins group lost the most weight at 12 months (4.7 kg - 10.3 lbs) compared to Ornish (2.2 kg - 4.9 lbs), Zone (1.6 kg - 3.5 lbs) and LEARN (2.6 kg - 5.7 lbs). However, the difference was not statistically significant at 12 months.
Conclusion: The Atkins group lost the most weight, although the difference was not statistically significant. The Atkins group had the greatest improvements in blood pressure, triglycerides and HDL. LEARN and Ornish (low-fat) had decreases in LDL at 2 months, but then the effects diminished.
13. Halyburton AK, et al. Low- and high-carbohydrate weight-loss diets have similar effects on mood but not cognitive performance. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2007.
Details: 93 overweight/obese individuals were randomized to either a low-carb, high-fat diet or a low-fat, high-carb diet for 8 weeks. Both groups were calorie restricted.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 7.8 kg (17.2 lbs), while the low-fat group lost 6.4 kg (14.1 lbs). The difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost more weight. Both groups had similar improvements in mood, but speed of processing (a measure of cognitive performance) improved further on the low-fat diet.
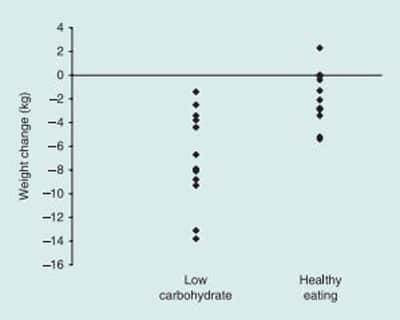
14. Dyson PA, et al. A low-carbohydrate diet is more effective in reducing body weight than healthy eating in both diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Diabetic Medicine, 2007.
Details: 13 diabetic and 13 non-diabetic individuals were randomized to a low-carb diet or a "healthy eating" diet that followed the Diabetes UK recommendations (a calorie restricted, low-fat diet). Study went on for 3 months.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 6.9 kg (15.2 lbs), compared to 2.1 kg (4.6 lbs) in the low-fat group.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost more weight (about 3 times as much). There was no difference in any other marker between groups.
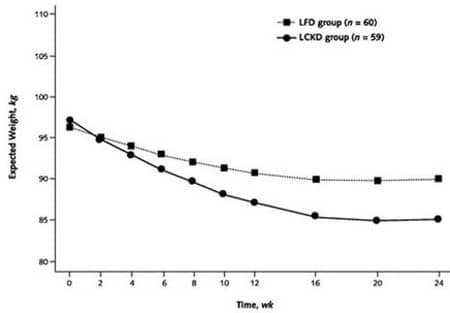
15. Westman EC, et al. The effect of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-glycemic index diet on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrion & Metabolism (London), 2008.
Details: 84 individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes were randomized to a low-carb, ketogenic diet or a calorie restricted low-glycemic diet. The study went on for 24 weeks.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost more weight (11.1 kg - 24.4 lbs) compared to the low-glycemic group (6.9 kg - 15.2 lbs).
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost significantly more weight than the low-glycemic group. There were several other important differences:
- Hemoglobin A1c went down by 1.5% in the LC group, compared to 0.5% in the low-glycemic group.
- HDL cholesterol increased in the LC group only, by 5.6 mg/dL.
- Diabetes medications were either reduced or eliminated in 95.2% of the LC group, compared to 62% in the low-glycemic group.
- Many other health markers like blood pressure and triglycerides improved in both groups, but the difference between groups was not statistically significant.
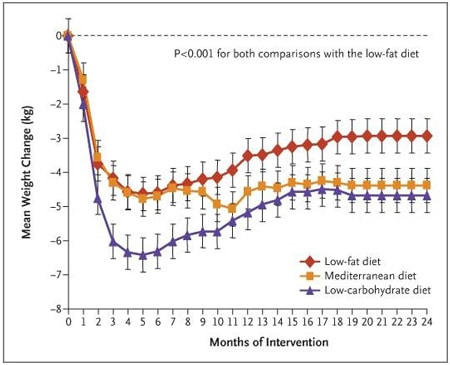
16. Shai I, et al. Weight loss with a low-carbohydrate, Mediterranean, or low-fat diet. New England Journal of Medicine, 2008.
Details: 322 obese individuals were randomized to three diets: a low-carb diet, a calorie restricted low-fat diet and a calorie restricted Mediterranean diet. Study went on for 2 years.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 4.7 kg (10.4 lbs), the low-fat group lost 2.9 kg (6.4 lbs) and the Mediterranean diet group lost 4.4 kg (9.7 lbs).
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost more weight than the low-fat group and had greater improvements in HDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
17. Keogh JB, et al. Effects of weight loss from a very-low-carbohydrate diet on endothelial function and markers of cardiovascular disease risk in subjects with abdominal obesity.American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2008.
Details: 107 individuals with abdominal obesity were randomized to a low-carb or a low-fat diet. Both groups were calorie restricted and the study went on for 8 weeks.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 7.9% of body weight, compared to the low-fat group which lost 6.5% of body weight.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost more weight and there was no difference between groups on Flow Mediated Dilation or any other markers of the function of the endothelium (the lining of blood vessels). There was also no difference in common risk factors between groups.
18. Tay J, et al. Metabolic effects of weight loss on a very-low-carbohydrate diet compared with an isocaloric high-carbohydrate diet in abdominally obese subjects. Journal of The American College of Cardiology, 2008.
Details: 88 individuals with abdominal obesity were randomized to a very low-carb or a low-fat diet for 24 weeks. Both diets were calorie restricted.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost an average of 11.9 kg (26.2 lbs), while the low-fat group lost 10.1 kg (22.3 lbs). However, the difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost more weight. Triglycerides, HDL, C-Reactive Protein, Insulin, Insulin Sensitivity and Blood Pressure improved in both groups. Total and LDL cholesterol improved in the low-fat group only.
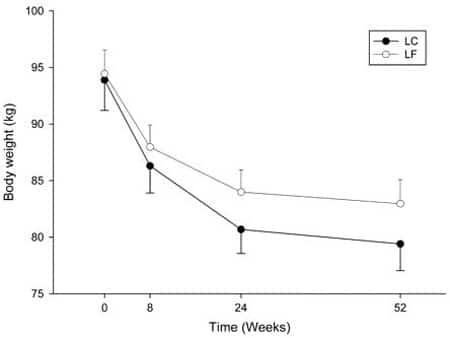
19. Volek JS, et al. Carbohydrate restriction has a more favorable impact on the metabolic syndrome than a low fat diet. Lipids, 2009.
Details: 40 subjects with elevated risk factors for cardiovascular disease were randomized to a low-carb or a low-fat diet for 12 weeks. Both groups were calorie restricted.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 10.1 kg (22.3), while the low-fat group lost 5.2 kg (11.5 lbs).
Conclusion: The low-carb group lost almost twice the amount of weight as the low-fat group, despite eating the same amount of calories.
This study is particularly interesting because it matched calories between groups and measured so-called "advanced" lipid markers. Several things are worth noting:
- Triglycerides went down by 107 mg/dL on LC, but 36 mg/dL on the LF diet.
- HDL cholesterol increased by 4 mg/dL on LC, but went down by 1 mg/dL on LF.
- Apolipoprotein B went down by 11 points on LC, but only 2 points on LF.
- LDL size increased on LC, but stayed the same on LF.
- On the LC diet, the LDL particles partly shifted from small to large (good), while they partly shifted from large to small on LF (bad).
20. Brinkworth GD, et al. Long-term effects of a very-low-carbohydrate weight loss diet compared with an isocaloric low-fat diet after 12 months. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2009.
Details: 118 individuals with abdominal obesity were randomized to a low-carb or a low-fat diet for 1 year. Both diets were calorie restricted.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 14.5 kg (32 lbs), while the low-fat group lost 11.5 kg (25.3 lbs) but the difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: The low-carb group had greater decreases in triglycerides and greater increases in both HDL and LDL cholesterol, compared to the low-fat group.
21. Hernandez, et al. Lack of suppression of circulating free fatty acids and hypercholesterolemia during weight loss on a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2010.
Details: 32 obese adults were randomized to a low-carb or a calorie restricted, low-fat diet for 6 weeks.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 6.2 kg (13.7 lbs) while the low-fat group lost 6.0 kg (13.2 lbs). The difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: The low-carb group had greater decreases in triglycerides (43.6 mg/dL) than the low-fat group (26.9 mg/dL). Both LDL and HDL decreased in the low-fat group only.
22. Krebs NF, et al. Efficacy and safety of a high protein, low carbohydrate diet for weight loss in severely obese adolescents. Journal of Pediatrics, 2010.
Details: 46 individuals were randomized to a low-carb or a low-fat diet for 36 weeks. Low-fat group was calorie restricted.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost more weight and had greater decreases in BMI than the low-fat group.
Conclusion: The low-carb group had greater reductions in BMI. Various biomarkers improved in both groups, but there was no significant difference between groups.
23. Guldbrand, et al. In type 2 diabetes, randomization to advice to follow a low-carbohydrate diet transiently improves glycaemic control compared with advice to follow a low-fat diet producing a similar weight loss. Diabetologia, 2012.
Details: 61 individuals with type 2 diabetes were randomized to a low-carb or a low-fat diet for 2 years. Both diets were calorie restricted.
Weight Loss: The low-carb group lost 3.1 kg (6.8 lbs), while the low-fat group lost 3.6 kg (7.9 lbs). The difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: There was no difference in weight loss or common risk factors between groups. There was significant improvement in glycemic control at 6 months for the low-carb group, but compliance was poor and the effects diminished at 24 months as individuals had increased their carb intake.
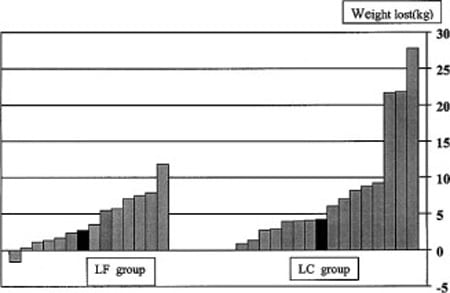
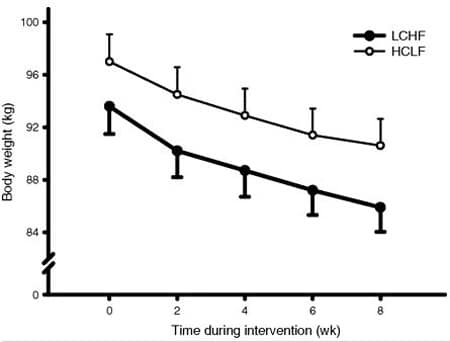
Here is a graph that shows the difference in weight loss between studies. 21 of 23 studies reported weight loss numbers:
The majority of studies achieved statistically significant differences in weight loss (always in favor of low-carb). There are several other factors that are worth noting:
- The low-carb groups often lost 2-3 times as much weight as the low-fat groups. In a few instances there was no significant difference.
- In most cases, calories were restricted in the low-fat groups, while the low-carb groups could eat as much as they wanted.
- When both groups restricted calories, the low-carb dieters still lost more weight (7, 13, 19), although it was not always significant (8, 18, 20).
- There was only one study where the low-fat group lost more weight (23) although the difference was small (0.5 kg - 1.1 lb) and not statistically significant.
- In several of the studies, weight loss was greatest in the beginning. Then people start regaining the weight over time as they abandon the diet.
- When the researchers looked at abdominal fat (the unhealthy visceral fat) directly, low-carb diets had a clear advantage (5, 7, 19).
Two of the main reasons why low-carb diets are so effective for weight loss are the high protein content, as well as the appetite-suppressing effects of the diet. This leads to an automatic reduction in calorie intake.
You can read more about why this diet works here: Why do Low Carb Diets Work? The Mechanism Explained.
Despite the concerns expressed by many people, low-carb diets generally do not raise Total and LDL cholesterol levels on average.
Low-fat diets do lower Total and LDL cholesterol, but it is usually only temporary. After 6 to 12 months, the difference is not statistically significant.
There have been some anecdotal reports by doctors who treat patients with low-carb diets, that they can lead to increases in LDL cholesterol and some advanced lipid markers for a small percentage of individuals.
However, none of the studies above noted such adverse effects. The few studies that looked at advanced lipid markers (5, 19) only showed improvements.
One of the best ways to raise HDL cholesterol levels is to eat more fat. For this reason, it is not surprising to see that low-carb diets (higher in fat) raise HDL significantly more than low-fat diets.
Having higher HDL levels is correlated with improved metabolic health and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease. Having low HDL levels is one of the key symptoms of the metabolic syndrome.
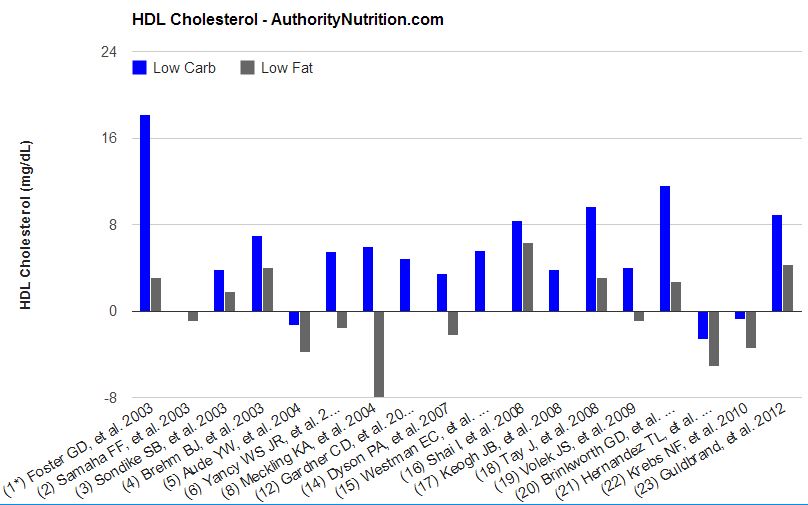
18 of the 23 studies reported changes in HDL cholesterol levels.
You can see that low-carb diets generally raise HDL levels, while they don't change as much on low-fat diets and in some cases go down.
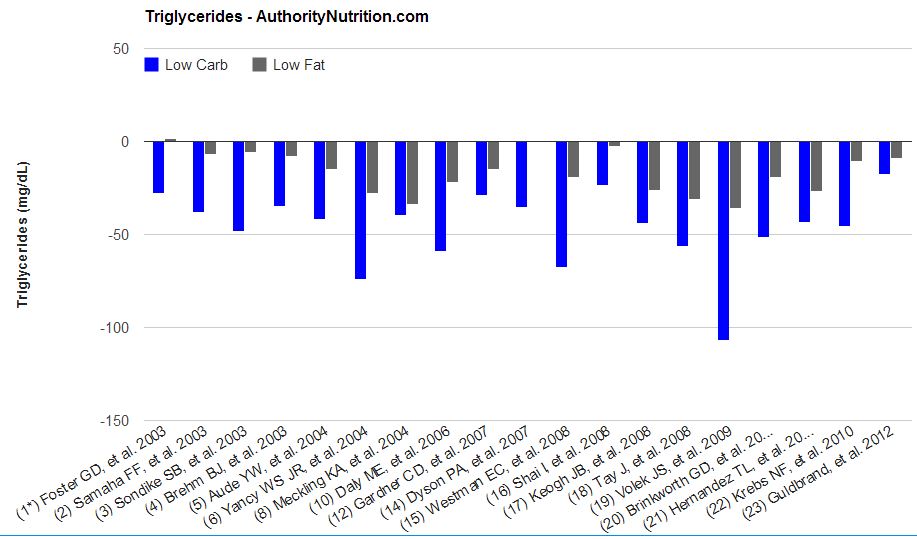
Triglycerides are an important cardiovascular risk factor and another key symptom of the metabolic syndrome.
The best way to reduce triglycerides is to eat less carbohydrates, especially sugar.
19 of 23 studies reported changes in blood triglyceride levels.
It is clear that both low-carb and low-fat diets lead to reductions in triglycerides, but the effect is much stronger in the low-carb groups.
In non-diabetics, blood sugar and insulin levels improved on both low-carb and low-fat diets and the difference between groups was usually small.
3 studies compared low-carb and low-fat diets in Type 2 diabetic patients.
Only one of those studies had good compliance and managed to reduce carbohydrates sufficiently. This lead various improvements and a drastic reduction in HbA1c, a marker for blood sugar levels (15).
In this study, over 90% of the individuals in the low-carb group managed to reduce or eliminate their diabetes medications.
A common problem in weight loss studies is that many people abandon the diet and drop out of the studies before they are completed.
I did an analysis of the percentage of people who made it to the end of the study in each group. 19 of the 23 studies reported this number:
The average percentage of people who made it to the end of the studies were:
Average for the low-carb groups: 79.51%
Average for the low-fat groups: 77.72%
Not a major difference, but it seems clear from these studies that low-carb diets are at the very least NOT harder to stick to than other diets.
The reason may be that low-carb diets appear to reduce hunger (9, 11) and participants are allowed to eat until fullness.
This is an important point, because low-fat diets are usually calorie restricted and require people to weigh their food and count calories.
Individuals also lose more weight, faster, on low-carb. This may improve motivation to continue on the diet.
Despite the concerns expressed by many health experts in the past, there were zero reports of serious adverse effects that were attributable to either diet.
Overall, the low-carb diet was well tolerated and had an outstanding safety profile.
Keep in mind that all of these studies are randomized controlled trials, the gold standard of science. All are published in respected, peer-reviewed medical journals.
These studies are scientific evidence, as good as it gets, that low-carb is much more effective than the low-fat diet that is still being recommended all over the world.
It is time to retire the low-fat fad!






Out Of Topic Show Konversi KodeHide Konversi Kode Show EmoticonHide Emoticon