A lot of people need to lose weight.
Unfortunately, it is not always easy to achieve and long-term success is rare.
All sorts of things are claimed to help with this... diets, potions and pills that are supposed to make things easier.
One of them is called glucomannan, a natural dietary fiber that is claimed to be an effective weight-loss supplement.
This article takes a detailed look at the science behind glucomannan and whether it is something you should be taking.
Glucomannan is a natural, water-soluble dietary fiber extracted from the roots of the elephant yam, also known as konjac.
It is available as a supplement, in drink mixes and is also added to food products, such as pasta and flour. It is also the main ingredient in shirataki noodles.
Glucomannan comprises 40% of the dry weight of the elephant yam, which is originally from Southeast Asia. It has a long history of use in herbal mixtures and traditional foods like tofu, noodles, and konjac jelly.
After the fiber has been extracted from the plant, it looks something like this:
In addition to being sold as a dietary supplement, it is used as a food additive -- an emulsifier and thickener denoted with the E-number E425-ii.
Glucomannan has an exceptional ability to absorb water and is one of the most viscous dietary fibers known.
It absorbs so much liquid that if you empty a glucomannan capsule into a small glass of water, the entire thing turns into a gel. These unique properties are believed to mediate its effects on weight loss.
BOTTOM LINE:Glucomannan is a water-soluble dietary fiber, extracted from the roots of the elephant yam. It has recently gained considerable attention as an effective weight-loss supplement.
Glucomannan is a water-soluble dietary fiber.
Like other soluble fibers, it is believed to promote weight loss via several mechanisms (1):
- It has a very low calorie content.
- It takes up space in the stomach and promotes a feeling of fullness (satiety), reducing food intake at a subsequent meal.
- It delays emptying of the stomach, contributing to increased satiety (2).
- Like other soluble fibers, it reduces the absorption of protein and fat (3).
It also feeds the friendly bacteria in the intestine, which turn it into short-chain fatty acids like butyrate, shown to protect against fat gain in some animal studies (4, 5).
Feeding the friendly gut bacteria may also have other benefits, and some studies have shown a correlation between altered gut bacteria and body weight (6, 7).
These mechanisms are believed to be similar to the effects of other soluble fibers on weight loss.
However, glucomannan is different from other soluble fibers because it's even more viscous, which makes it particularly effective.
BOTTOM LINE:Like other soluble fibers, glucomannan absorbs water in the stomach and contributes to satiety. It may also promote reduced calorie intake and weight loss via several other mechanisms.
Studying mechanisms is always interesting, but what we really want to know is if this stuff leads to actual pounds being lost.
Fortunately, we have several randomized controlled trials on glucomannan. These types of studies are the "gold standard" of scientific experimentation in humans.
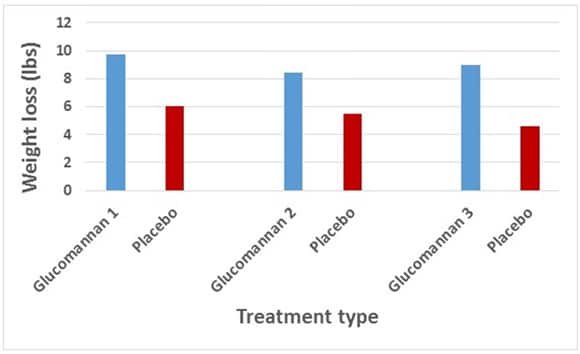
In the biggest one, 176 healthy overweight people were randomly assigned to ingest either a supplement with glucomannan, or placebo (a dummy pill), while on a calorie-restricted diet (8).
Three different glucomannan supplements were tested, with varying dosages. Some also had other fibers added to them.
These were the results after 5 weeks:
As you can see, weight loss was significantly greater in the glucomannan groups.
There are several other studies that agree with this. Glucomannan causes modest weight loss in overweight and obese individuals when regularly ingested before a meal (9, 10, 11).
It is especially effective when combined with a weight-reducing diet. The same applies to all weight-loss methods... they work best in combination.
BOTTOM LINE:When taken before meals, glucomannan may lead to modest weight loss in overweight individuals, mainly by creating a feeling of fullness and reducing energy intake.
In addition to promoting weight loss, glucomannan may improve a number of risk factors for heart disease.
According to a systematic review of 14 studies, glucomannan can (10):
- Lower total cholesterol by 19 mg/dL (0.5 mmol/L).
- Lower LDL cholesterol by 16 mg/dL (0.4 mmol/L).
- Lower triglycerides by 11 mg/dL (0.12 mmol/L).
- Fasting blood sugar by 7.4 mg/dL (0.4 mmol/L).
The main mechanism by which it reduces blood cholesterol is by decreasing absorption of cholesterol in the gut.
According to these studies, adding glucomannan to your diet could potentially lower the risk of developing heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Being a water-soluble fiber, glucomannan has also been successfully used to treat constipation (12, 13).
BOTTOM LINE:Glucomannan can cause improvements in several important risk factors for heart disease, including total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides and fasting blood sugar.
For weight loss, a dosage of 1 gram, 3 times per day is considered sufficient (14).
In contact with water, glucomannan expands and can absorb up to 50 times its weight. Therefore, the recommended dosage of glucomannan is lower compared to other fiber supplements.
Glucomannan does not have any effect on weight loss unless it is taken before a meal. Timing recommendations range from 15 minutes to 1 hour before a meal (14, 8).
Glucomannan is well tolerated and is generally considered safe.
However, if glucomannan expands before reaching the stomach, it may cause choking or blockage of the throat and esophagus (the tube that moves food from your mouth to your stomach).
To prevent this, it should be washed down with 1-2 glasses of water or other liquid.
Some people may experience mild side effects, such as bloating, flatulence, soft stools or diarrhea, but this is usually uncommon.
Glucomannan can also reduce the absorption of oral medications like sulfonylurea, a diabetes drug. This can be avoided by taking the medication at least 4 hours after or one hour before ingesting glucomannan.
According to the evidence, glucomannan is an effective weight-loss supplement. But same as with pretty much any weight-loss strategy, it doesn't work in isolation.
The only known way to lose weight in the long-term, is to make a permanent change to your lifestyle.
Glucomannan may help make that easier, but it won't work any miracles on its own.


Out Of Topic Show Konversi KodeHide Konversi Kode Show EmoticonHide Emoticon